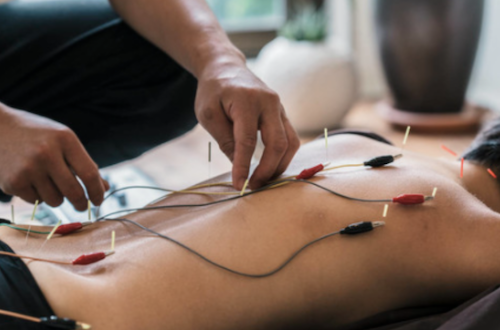
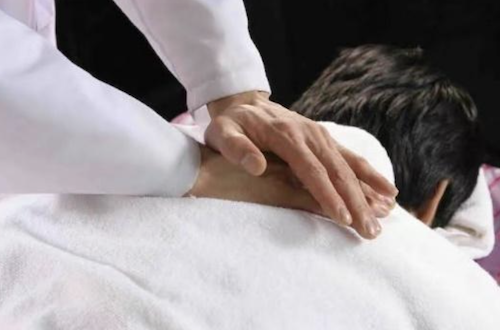
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
TCM is a fully institutionalised part of Chinese health care and is widely used in western medicine. TCM includes herbal medicine, acupuncture, moxibustion, Tuina, food therapy, and physical exercises, such as Qigong. Like western medicine, TCM is a general practice that can treat a variety of diseases and illnesses. TCM is mainly divided into internal medicine, surgery, gynecology, and pediatrics in Chinese Medicine Hospitals.